In the diverse landscape of the United States, the process of obtaining a driver’s license can vary dramatically from one state to another. While some states, like Georgia, emphasize a stringent set of requirements and lengthy testing processes, others may adopt a more lenient approach, allowing faster results. This patchwork of rules means that a new driver in California might face vastly different challenges and expectations than a peer in Texas or New York.
The implications of these discrepancies extend beyond just the testing process and include regional variations in licensing that influence safety, accessibility to driving, and even insurance rates. In this article, we will delve into the notable disparities in driver licensing rules across states, exploring how these differences shape the driving experience for millions of Americans and what it means for aspiring drivers navigating this complicated terrain.
The Impact of Lenient Driver’s Licensing Rules
Lenient driver’s licensing rules can significantly influence the number of inexperienced drivers on the roads, raising safety concerns. States that implement less stringent qualifications and testing requirements often see a higher prevalence of new drivers who may not be adequately prepared for the challenges of driving. For example, states with minimal testing requirements or loopholes that allow for quicker licensing are often associated with increased accident rates among youthful and inexperienced drivers.
Statistics reveal troubling correlations. A study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) indicates that states with robust Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) laws, which impose stricter requirements on new drivers, report a 63% reduction in fatal crashes among 15-17-year-olds in some regions. This suggests that areas with lenient rules lack essential protective measures against inexperience, exposing the public to higher risks on the roads [IIHS].
Moreover, research conducted by the Highway Loss Data Institute revealed that regions with poor GDL frameworks saw a 20% increase in claim frequencies among 16-year-old drivers when compared to states with effective GDL laws [IIHS]. Allowing early access to driving permits can also lead to unintended health consequences, as studies have shown statewide increases in drug-related and mental health-related mortality among adolescents following the facilitation of earlier driving eligibility [arxiv.org].
The findings suggest a clear link between lenient driver’s licensing policies and higher rates of accidents involving inexperienced drivers. While granting access to driving offers mobility and independence, the trade-off in safety is a pressing issue. As states contemplate their licensing rules, understanding the implications on novice driver competence becomes crucial in shaping a safer driving environment for all.
| State | Written Test Required | Practical Test Required | Average Time to Get Licensed |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| Texas | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| New York | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| Florida | Yes | Yes | 3 months |
| Georgia | Yes | Yes | 1 year |
| Illinois | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| Virginia | Yes | Yes | 9 months |
| Pennsylvania | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| Ohio | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
| Michigan | Yes | Yes | 6 months |
This table contrasts the licensing requirements across different states, including whether a written and practical test is required as well as the average expected time for new drivers to receive their licenses.
The Benefits of Stricter Licensing Rules
Stricter driver’s licensing regulations have been shown to significantly improve road safety by ensuring that only qualified drivers are allowed on the road. One of the most effective systems is the Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) program, which defines a staged approach to licensing new drivers, allowing them to gain experience in lower-risk conditions.
Evidence and Expert Opinions
Research indicates that GDL systems can lead to a substantial reduction in fatal crashes among teenage drivers. For instance, states with comprehensive GDL laws have reported decreases in teen crash rates by as much as 30%. This is further supported by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), which emphasizes that robust laws are pivotal in minimizing risks that inexperienced drivers face.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also aligns with these findings, stating that programs aimed at reducing teen crashes are predicated on less risky driving environments, marking significant progress in protecting vulnerable young drivers.
Statistical Support
Statistics demonstrate that implementing stricter rules can drastically reduce accident rates. For example, New Jersey’s GDL policy led to a 14% reduction in overall collisions and a 25% decrease in fatal accidents specifically among 17-year-olds.
Components of GDL, such as nighttime driving restrictions, play crucial roles. Research shows these restrictions can reduce nighttime fatal crash incidents for younger drivers by about 10%. Another significant component is the requirement for driver education, which includes proper behind-the-wheel training. Studies have indicated that drivers who engaged in formal educational requisite had crash rates up to 27% lower than those who did not, highlighting the importance of rigorous preparatory measures in the licensing process.
Public favor has also shifted towards stricter licensing protocols, with surveys indicating that a majority of motorists support graduated licensing systems. These preferences may reflect a broader understanding of the need for enhanced oversight in the formative years of a driver’s journey.
Moreover, comparative studies illustrate that stricter regulations correlate with lower accident rates across states. For instance, states implementing stringent seat belt laws not only achieve higher compliance rates but also report reduced fatalities—consenting that robust traffic laws save lives.
In conclusion, as traffic laws evolve, the call for stricter licensing rules remains pressing. Moving toward enhanced testing and educational requirements for new drivers serves to empower safer driving practices and secure a more accident-free environment on the roads for everyone.
International Comparisons of Driver’s Licensing Processes
Understanding how different countries approach the task of licensing drivers reveals much about their priorities regarding road safety, accessibility, and the preparation of new drivers. Examining the driver’s licensing processes in countries such as China, Uganda, Egypt, Australia, Burundi, Japan, and Russia provides insights into the vast discrepancies in requirements, testing procedures, and overall pass rates.
China
- Requirements: In China, obtaining a driver’s license includes passing a complex series of tests.
- Testing Processes: Applicants must complete:
- A written theory test containing 100 questions, with a minimum pass rate of 90%.
- A practical driving skills test on a designated obstacle course.
- A real-world driving test to assess practical driving abilities.
- Pass Rates: The specific pass rates are not easily accessible, but the rigorous process suggests a focused effort on ensuring driver competency.
Uganda
- Requirements: Uganda’s testing process is significantly simpler.
- Testing Processes: The theoretical assessment only includes 30 questions.
- Pass Rates: A minimum correct answer percentage of just 25% is required to pass this examination, highlighting a lenient standard that may influence skills on the road.
Egypt
- Requirements: Like Uganda, Egypt has a basic licensing structure.
- Testing Processes: The written test comprises just 10 questions.
- Pass Rates: The lenient structure indicates a potentially higher number of inadequately skilled drivers on the roads due to insufficient evaluation methods.
Australia
- Requirements: In contrast, Australia imposes more rigid preparation.
- Testing Processes: Prospective drivers may need to document over 120 hours of supervised driving before the practical test in some states, ensuring comprehensive skill-building.
- Pass Rates: The pass rates vary by state but hover around 57% for first-time attempts in New South Wales, reflecting the thorough nature of the testing protocol.
Burundi
- Requirements: The standards are minimal in Burundi.
- Testing Processes: Candidates can access driving privileges without required training or recorded practice hours, often resulting in significant road safety challenges.
- Pass Rates: The lack of testing rigor correlates with a high rate of unlicensed drivers on the roads.
Japan
- Requirements: Japan features a highly structured and demanding licensing process.
- Testing Processes: Applicants face:
- A theory test that consists of 50 questions, demanding a score of 90% for success.
- A highly regulated practical test that imposes immediate failure for even minor infractions, such as exceeding speed limits by 19 mph.
- Pass Rates: Approximately 55% of candidates pass the practical test, indicating the stringent nature of the process.
Russia
- Requirements: Russia maintains a robust examination protocol.
- Testing Processes: The licensing process mandates completion of both a theoretical exam and two practical assessments (closed course and public roads).
- Pass Rates: While specific pass rates are not provided, the dual practical testing structure is indicative of a thorough evaluation system.
Conclusion
The comparative analysis of international driver licensing processes highlights significant disparities in requirements and evaluations, reflecting each country’s unique regulatory environment and commitment to road safety. Nations like Japan and Australia adopt thorough and challenging approaches, while others like Uganda and Burundi maintain less rigorous standards, raising questions about driver preparedness and safety on the roads. As global traffic continues to increase, the importance of robust driver licensing mechanisms becomes more critical in ensuring safer driving environments worldwide.
‘Earning the coveted license to drive is a big moment in life as it represents a maturity milestone, but most importantly, it means freedom.’ This quote captures the essence of driver licensing; it signifies not only a legal requirement but also an important step toward personal freedom and responsibility that comes with the ability to drive.
Conclusion
In summary, the landscape of driver licensing in the United States is characterized by significant state-by-state variability that directly impacts safety and accessibility for drivers. The article has highlighted how divergent requirements, such as testing processes and qualifications, can lead to increased risks on the roads, especially for inexperienced drivers. Stricter regulations, as evidenced by the effectiveness of Graduated Driver Licensing programs, contribute to a notable decrease in accident rates, underscoring the importance of rigorous preparation for new drivers. Conversely, more lenient rules may facilitate quicker access to a driver’s license but often exacerbate safety challenges. Therefore, understanding these regulations is not merely a matter of compliance; it plays a critical role in ensuring safe driving practices and promoting personal freedom.
Key Takeaways:
- State Variability: Different states have varying requirements and regulations influencing drivers’ preparedness.
- Safety and Regulation: Stricter regulations correlate with lower accident rates, particularly among inexperienced drivers.
- Graduate Licensing Programs: Implementation of such programs is crucial for enhancing safety and promoting better driving practices.
- Liability and Compliance: A thorough understanding of licensing procedures is vital for informed driving decisions and road safety.
- Freedom vs Safety: The balance between access to driving and ensuring safety is pivotal as states navigate their licensing policies.
By navigating this complex terrain of driver licensing effectively, individuals can better appreciate the significant implications these rules have on their safety and mobility, reinforcing the idea that informed drivers contribute to a safer road environment for all.
User Adoption and the Impact of Licensing Changes on Road Safety
Research has shown a strong correlation between changes in driver’s licensing regulations and the resulting impact on user behavior and road safety:
- Youth Access to Driving: States that allow learner’s permits before the age of 16 have seen troubling outcomes, including a notable increase in adolescent drug-related and mental health-related mortalities. Specifically, a study indicated an increase of 1.331 per 100,000 in drug-related mortality among young females, attributed to expanded access to driving.
- Enhanced Driver Licensing Programs: In Ohio, an enhancement to the Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) law in 2007 led to an 18% decrease in crash rates for 16- to 17-year-olds, compared to older age groups, emphasizing the benefit of stricter licensing regulations in reducing accidents.
- Impacts on Older Driver Policies: A study noted that looser in-person renewal requirements for drivers aged 65-74 correlated with an 8% increase in crash rates, and extending renewal periods for those aged 75 and older was linked to an 18% increase in injury rates, suggesting that too lax renewal policies can have adverse effects.
- Importance of Timing in Licensing: Data from Ohio highlighted that young drivers licensed at age 16 had a 27% lower crash rate in the two months following licensure compared to those who obtained their license at 18, reinforcing the importance of early and comprehensive training.
- Success of California’s GDL Program: Following the implementation of California’s GDL system in 1998, the state observed a significant drop in fatal and severe injury crash rates among 16- and 17-year-olds, demonstrating the effectiveness of graduated licensing in enhancing road safety for young drivers.
These insights underline the critical role that thoughtful licensing regulations play in shaping driver preparedness and ultimately, road safety outcomes. Policymakers should consider these findings when debating changes to licensing frameworks.
Licensing Requirements Graphics
To enhance your understanding of the varied licensing requirements, here are graphics that visually represent the data:
This graphic depicts the differences in driver’s licensing requirements across the United States, including testing and application requirements.
This infographic compares international driver’s licensing requirements, illustrating the various approaches taken by different countries.
Effects of Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) Laws
The implementation of Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) laws has had a significant positive impact on road safety, especially among novice drivers. These laws have been designed to gradually introduce new drivers to the complexities of driving, allowing them to gain critical experience in a controlled manner.
- Reduced Accident Rates: Research indicates that states with strong GDL laws have observed substantial decreases in accident rates among teenage drivers. For instance, GDL programs have been linked to a 68% reduction in fatal crashes for 16-year-old drivers nationally, demonstrating the effectiveness of these laws in improving safety on the roads.
- Structured Training Programs: GDL laws often mandate structured training and supervised driving hours, which help prepare novice drivers for real-world challenges. States such as California and New York have implemented these structured requirements, resulting in a marked reduction in teen crash rates. For example, California noted a 17-28% decrease in fatal and injury crashes for young drivers after GDL laws were introduced.
- Public Support for GDL Laws: The GDL framework enjoys considerable public support, as many recognize the connection between stricter licensing regulations and enhanced road safety. Surveys indicate that motorists overwhelmingly favor graduated licensing systems, understanding that these measures are crucial for reducing the risks associated with inexperienced drivers.
Below is a graph illustrating the reduction in accident rates over time as GDL laws were implemented across various states:
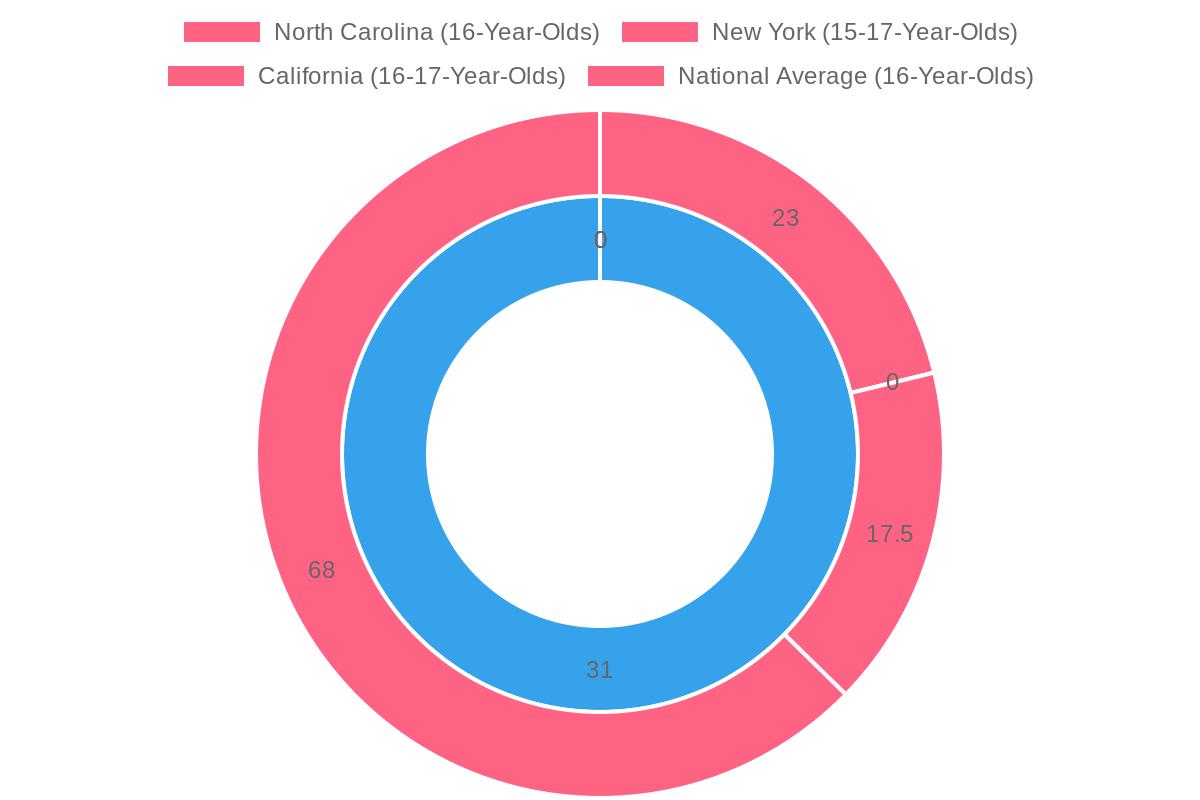
This graph highlights how GDL laws have effectively reduced fatal crashes among young drivers, reinforcing the crucial role these regulations play in promoting safer driving practices.
In conclusion, the effects of GDL laws underscore the importance of comprehensive driver education and structured licensing processes in safeguarding public road safety. As states consider their licensing regulations, it is vital to recognize the proven benefits of GDL laws and their contribution to reducing accidents among novice drivers.
External Links for Credibility
To enhance the credibility of the statistics and claims made in the article, please refer to the following authoritative sources:
- Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS): The IIHS has conducted extensive research on the effects of Graduated Driver Licensing (GDL) laws on collision claims and crash rates, demonstrating their effectiveness at reducing accidents among inexperienced drivers. Explore their studies on GDL benefits here and details about teen fatal crash rates here.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides resources on adolescent driver safety, including a GDL Planning Guide that confirms the positive effects of structured licensing systems on reducing crashes. More information can be found here.
- Additional relevant studies and citations from IIHS can be accessed here and here.
